■ ACMT/ 邱耀弘
前言
Legendofspecialtranslate:twopartspaperof “IntroductiontoMetallographicforPowder Metallurgy”wereshowedonPowderMetallurgy Review.PartItranslatedbyDr.QandPartIItranslated byDr.DanofPIMA-CN.專案翻譯說明:本文章為刊 載於英國國際期刊粉末冶金回顧 (PowderMetallurgy Review)的期刊中連載二期的技術文件,由PIMA-CN 的邱耀弘博士與鄧忠勇博士(現於上海富馳高科技任職) 個別翻譯。
編者說明(Dr. Q)
金相分析技術其實算是微結構觀察中的一門重要技術, 已經不是單純的金屬微結構分析,而擴展到許多不同的 材料分析上。當然,觀察的主要工具仍舊以方便的光學 顯微鏡為主,目的在於方便工程師能夠因為樣品準備容 易,能夠快速定論以發現問題並加以修正錯誤。然而在 中國和台灣,許多PM與MIM公司的金相檢驗設備缺 乏甚至沒有金相分析的技術,那麼要做好PM與MIM 產品就相當困難,提出的品質數據也將令人懷疑。編者 希望拋磚引玉的協助大中華地區的PM與MIM廠家, 盡快的建立好金相分析技術,來提升自己的產品良率和 技術。
The Author 原作者
ThomasF.Murphy,FAPMI,Scientist,Research &DevelopmentHoeganaesCorporation Cinnaminson,NJUSA Email:tom.murphy@hoeganaes.com
Part 1 Sample preparation techniques
第一部分 樣品備製技術
文章出處︰P29~37,Vol.3No.4,©2014Inovar CommunicationsLtd,Winter2014,Powder MetallurgyReview 注意翻譯按照有關英式英文內容以更改為美式英文,請對照英文原文敘述,有錯誤與不懂之處,歡迎討 論!藍色字體為譯者與編者補充說明。 譯者:邱耀弘博士(Dr.Q),當時是台灣鐿鈦科技顧問/ 深圳鑫迪科技有限公司技術長,2016/05/06


Metallographicisthestudyofthephysicalstructure ofmetalsusingmicroscopy.Theprocesshasmany advantagesasamethodtocharacterizePowder Metallurgyproductsandhelpstoensureproduct qualityandunderstandissuesthatarise.Thecorrect preparationofsamplesinvolvesanumberofcritical stepsandisessentialforaccurateresults. InpartoneofourIntroductiontoMetallographicfor PowderMetallurgy,ThomasFMurphy,Hoeganaes Corporation,USA,oneofthePMindustry’smost recognizedmetallographers,looksathowbestto preparesamplesfortheprocess.
金相,是一種通過顯微鏡來研究金屬物理結構的技 術,可以用金相技術來表現粉末冶金製品的組織特 性,以及說明我們如何進行粉末冶金產品的品質控制 和解決製程中的問題。本文中來自美國赫格納斯公司 的Mr.ThomasFMurphy,他將為我們介紹如何運用 這項技術來揭露和檢查粉末冶金樣品的顯微組織。
AsmanufacturersandusersofPowderMetallurgy (PM)materials,ourmissionasanindustryis todevelopandproduceproductsthatmeet, andwherepossible,exceedourcustomers’ expectationsandrequirements.Inorderto accomplishthisgoal,wemustevaluateour productsonaperiodicandsystematicbasisusing alltheavailabletesttechniques.Thisevaluation requirementalsoextendstoend-users,those innewproductdevelopmentandresearchers, wheretheattributesthatinfluenceanddetermine thepropertiesaredefined.Physical,mechanical, chemical,andmetallographictestsaresomeof themethodsusedmostoftentocharacterisePM products.Oftheaforementionedtesttechniques, Metallographicisprobablythemosteffectiveand efficientdiagnostictoolconsideringtheamount ofrelevantinformationgeneratedcompared withIntroductiontoMetallographicforPowder Metallurgy: 對於我們是粉末冶金材料的製造和使用者而言,作為 此個行業的使命是開發和生產產品,在所有可能的情 況下,滿足並超越客戶的期望和要求。為了實現這一目標,我們必須定期在有系統的基礎上,利用所有可 用的測試技術,來作為我們的產品所必須的評價,這 一個評價要求也會延伸到最終用戶。對那些在新產品 開發和研究人員來說,有關產品其所擁有的特性,以 了解其影響並確定特性的定義。包含物理、機械、化 學和金相檢驗,這些手段是最常用的方法來描述產品 的特性。上述試驗技術中,金相分析可能是最有效的 診斷工具,我們結合相關的資訊,把傳統材料料與粉 末冶金金相比較介紹如下:

Part1,Samplepreparationtechniques Metallographicisthestudyofthephysicalstructure ofmetalsusingmicroscopy.Theprocesshasmany advantagesasamethodtocharacterizePowder Metallurgyproductsandhelpstoensureproduct qualityandunderstandissuesthatarise.Thecorrect preparationofsamplesinvolvesanumberofcritical stepsandisessentialforaccurateresults.Inpart oneofourIntroductiontoMetallographicfor PowderMetallurgy,ThomasFMurphy,Hoeganaes Corporation,USA,oneofthePMindustry’smost
recognizedmetallographers,looksathowbestto preparesamplesfortheprocess.Investmentsin bothmanpowerandequipment.Metallographic isprimarilyacollectionofvisualandimaging techniquesthatprovideaninsightintothehistory ofamaterialorpartanditsbehavior.
WithconsolidatedPMmaterials,wherethe propertiesarecontrolledbythedensity,the combinationofchemicalcompositionandalloying method,andthemicrostructure,Metallographic istheonlytestmethodcapableofproviding informationonallthreecontributors.Thisis accomplishedbytheexaminationofproperly selectedandpreparedmetallographicspecimens.
第1部分、金相樣品製備技術是金屬在顯微鏡下觀察 其物理結構的方法,這個備製技術具有許多優點,可 作為一種有效的方法來表現粉末冶金產品的性能,並 有助於確保產品品質和理解所出現的問題。正確的樣 品製備涉及許多關鍵的步驟,是獲得準確結果必不可 少的技術。在第一部分,我們介紹了金屬粉末冶金的金相,P1-Fig.1(P1- 圖 .1) 美國赫格納斯公司的 Mr. ThomasFMurphy,是當今粉末冶金業界最認可的金 相技術人員,將告訴讀者如何做最好的樣品備製。在 人力和設備兩方面的投資,金相顯微結構主要是收集 視覺和影像的技術,提供了一個可觀察到一種材料或 部件的製程行為與歷史,且可對於粉末冶金材料的密 度控制、化學成分和合金相結合的方法,提供三個資 訊可在同一個觀察得到結果的測試方法。這是通過正 確選擇和準備的金相試樣來檢測完成。
1.Sample preparation樣品準備
Metallicspecimensareopaqueand,asaresult, opticalexaminationmustbeperformedoncarefully preparedplanar(two-dimensional)surfaces.This preparationsequenceisnormallyseparatedinto severalwell-definedsteps.Theseare: 金屬樣品是不透明的,因此,對其進行光學檢查必須 仔細的準備的一個平面(二維的)表面。這個準備序 列通常被分為幾個定義明確的步驟。這些是: 1.1Sampleselection 樣品選擇 1.2Sectioning切片 1.3Mounting鑲埋 1.4Grinding&Polishing研磨與拋光 此外,Etchingand/orcoating蝕刻或塗層(放在第二 部分) Eachstepinthesequencemustbesuccessfully accomplishedbeforeprogressingtothenext.In mostcases,errorscommittedduringonestepin theprogressioncannotbecorrectedlaterinthe process.Adheringtothebestpossibleprocedures istheonlymeanstoproduceconsistent,reliable results.Basically,theeffectivenessofanexamination isultimatelydependentonthequalityofthesample preparation. 上述序列中的每一步都必須在進展到下一步之前有效 的完成。在大多數情況下,在過程中前一個步驟中犯 下的錯誤不能在以後的步驟中被修正。堅持盡可能的 做好每一步驟是唯一的方法,以產生一致且可靠的結 果。基本上,檢驗的有效性最終取決於樣品製備的品 質。
1.1 Sample selection樣品選擇
Whendesigningatestprogramme,theselectionof thesample(s)tobetestedisofprimaryimportance. Alltheskillandcareusedinsubsequentpreparation willbewastedifthesamplesdonotcontainthe desiredinformation.Thereareseveralreasonsfor selectingspecificsamples.Theseinclude: 在設計金相檢驗方案時,所選取的樣本是非常重要 的。如果不能包含所需要的資訊,所有的技能和整個 後續準備的工作將被浪費。選擇特定樣品的原因有幾 個。這些措施包括:
•Generalmicrostructuralanalysis:Processcontroltypetest,proportionsofmicrostructuralfeatures containedinthecross-section(s)shouldbe representativeofwhatisinthepartvolume. 一般顯微結構分析:製程控制類型的測試,在橫截面 中的微觀結構特徵的比例應在整體中有代表性。 •Failureanalysis:Partfailedinserviceorduring testing. 失效分析:在運行中和檢驗中發生部分失效的位置。
•Specificareaanalysis:Defectareaordifficultto manufactureregion. 特定區域分析:缺陷區或製造困難的區域。
Quantitativeanalysis:Partandcross-sectionisused torepresentthetypicalordesiredmicrostructure. Stereologicalorimageanalysistestingisusually performedonthesespecimens. 定量分析:部分和橫截面是用來代表典型的或期望的 顯微組織。通常對這些樣品進行體視學和圖像分析。
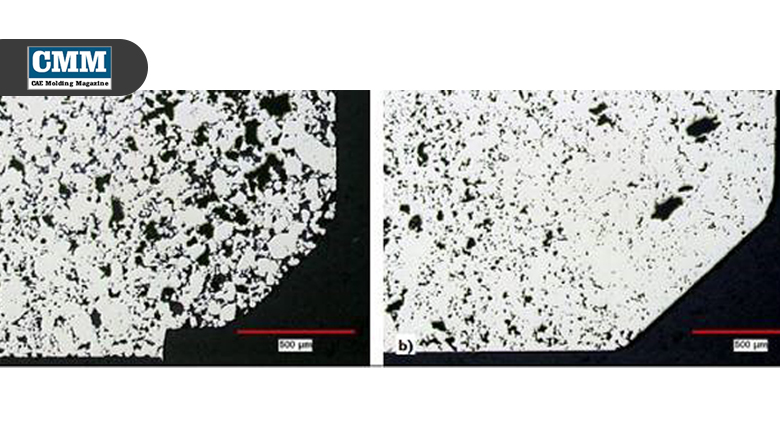
P1-Figs.2and3representcrosssectionalareas thatcouldfitintoseveralofthesampleselection categoriesmentionedabove.InP1-Fig.2(aandb), theresultsofchangesinpartdesign,diefill,and compactionareseenasalargedifferenceinlocal densityinthesamelocationofaredesignedpart.In P1-Fig.3,across-sectionthroughasurfacedefectis shown. P1-圖.2和P1-圖.3代表樣品橫截面的區域,可以配 合上述幾個樣品選擇類別的描述。在圖.2(a和b),代 表零件改變設計,對模具填充和壓實的變化,相同的 位置可以看到密度的差異。在P1-圖.3中,則是通過 一個表面缺陷的橫截面顯示圖。
Inbothfigures,thefeaturesshowncouldbe consideredthereasonforfailure,adefector difficulttomanufactureregion,orananomaly foundduringaprocess-controltest.Additionally, quantitativetestingcouldbeperformedonthe surfacestoprovidevaluesofthelocaldensity,size offeatures,specificlocations,etc.Inbothcases, priorknowledgeofthepartsisasignificantfactorin thesampleselection.Withthedensitydistribution issue,thiswasthelocationwhereahigherdensity wasdesired. 一個缺陷或難以製造的區域,或在製程控制檢驗中發 現的異常,就可以在這兩個圖中所示的特徵,找出產 品失敗的主因。此外,金相還可以進行定量測試其表 面上的局部密度、特徵(缺陷)的大小、具體位置等。 以此二圖來看,從密度分佈的問題來說,一個高密度 的位置是被金相照片所呈現出來,這便可能是缺陷的 位置。
InP1-Fig.3,thedefectwasvisiblefromthepart surface.AnotherdefecttypeisshowninP1-Fig.4. Itisanareashowingde-laminationsandcracks causedbydifficultieswithpowderandmaterialflow duringcompaction.Thelocationofthiscondition isprobablynotvisiblenoristhelocationapparent fromthepartsurface.Itmighthavebeenan isolatedregionorcharacteristicofacompaction problem.Y 在P1-圖.3中,缺陷是從零件表面可見的。另一種缺 陷類型如P1-圖.4所示,在壓實過程中的粉末及材料 流動困難,使這區域呈現出分層和裂紋。這種情況的 位置很有可能是看不到的,也不能從零件表面的位置 明顯看到。它可能是一個孤立的區域,或是位於一個 壓實體中的問題特徵。但是進行金相分析之後,便能 夠看到這樣的缺陷。■